Welcome to the complete, comprehensive guide to the Narrowband Internet of Things (NB-IoT) and how it has changed IoT services. In this guide, we’ll discuss NB-IoT’s benefits, uses, and possible futures. Let’s start this journey to find out how NB-IoT can change the way IoT services are provided.
What is NB-IoT?
The Internet of Things (IoT) has become a vital component of the modern digital age. This can be used in a number of sensor-based applications and has a handful of effects.
The primary objective of this technology was to make wireless data networks more valuable. These elements come up in a lot of distinct cellular and non-cellular ways, like in sensor networks, control networks, and distinct networks.
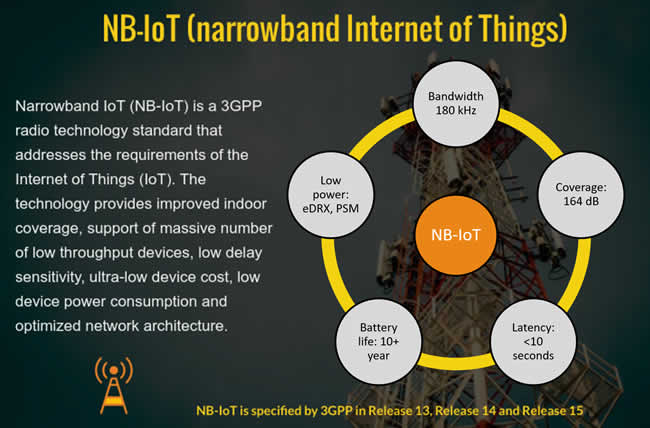
The Internet of Things (IoTs) can be different in the way they work. One type of IoT Service widely used is narrowband Internet of Things (NB-IoT). The Internet of Things (IoT) needs to use narrowband wavelengths in order to work. It’s better than some other Internet of Things (IoT) gadgets in a number of ways because it has limited speed. NB-IoT technology met the need for a standard that all wireless devices and services could use.
The Low-Power Wide-Area (LPWA) technology which sets up the Internet of Things is an important step ahead in the area of IoT interaction. Narrowband-IoT is different from regular cell phone networks because it uses an approved frequency. This means that battery-powered IoT devices will have better range, impact, and reliability. Narrowband’s design renders it possible to use plenty of various uses to send data quickly and easily, such as smart towns and industrial robotics.
Narrowband IoT services also do very well with other standards. NB-IoT was created to work with LTE. As its use in LTE networks has shown, and can be used in a lot of different situations.
Benefits of NB-IoT
Increased NB-IoT Data Rates and Reduced Power Consumption:
Narrowband Internet of Things (IoT), functions within a bandwidth of 200KHz, providing notable data transfer rates of up to 250kbps. This characteristic offers significant benefits in Internet of Things IoT applications, mainly when intermittent transmission of tiny data packets occurs over short distances. The intentional emphasis of NB IoT on reducing data rates directly enhances its remarkable energy efficiency and sustainability in IoT applications.
Enhanced Power Management Techniques:
NB-IoT uses Power Saving Mode (PSM) and Extended Discontinuous Reception to save power. These novel features boost IoT energy efficiency. Because of its long battery life and low maintenance expenses, NB IoT is ideal for large-scale IoT installations.
Open Standards for Effortless Integration:
It guarantees seamless integration of devices and networks by following worldwide open standards. Compliance supports easy IoT solution integration, enabling broad use of NB-IoT technology in the Internet of Things ecosystem.
Secure connectivity using licensed spectrum:
NB-IoT networks are safe, stable, and interference-free when using licensed spectrum. This is crucial for IoT applications that need reliable communication.
Practical Components for Economic Solutions:
NB-IoT devices use affordable components, making them a viable option for various IoT applications. This affordability decreases company and consumer entry barriers.
Excellent Urban and Indoor Immersion:
NB-IoT works well in cities and indoors because of its penetration. It efficiently transmits signals through thick walls and underground, assuring IoT connection.
Extended Battery Life and reduced Energy Use:
As NB-IoT minimizes energy usage, IoT devices have longer battery lives. This cuts battery replacements, making IoT more sustainable and cost-effective.
Comprehensive Coverage for Geographic Reach:
NB-IoT is suited for IoT applications that need comprehensive geographical coverage, including distant and rural regions. Innovative solutions are possible in varied geographic contexts.
Comparative analysis of the Internet of Things (NB-IoT) and other wireless communication approaches
As a result of the fast expansion of low-data-rate IoT services in an intelligent manner, LPWA technology is gaining more and more popularity in the business world, and its market share is progressively expanding. As stated in the study that Hequan Wu presented at the China Internet of Things Conference in 2016, intelligent Internet of Things applications may be divided into three groups according to the data transmission rate requirements that will be in place in the year 2020 or later.
HIGH RATE OF DATA TRANSFER:
The speed at which data is sent is faster than 10 Mbps. 3G, 4G, and Wi-Fi are the entry methods that can be used. They are used mainly in direct television broadcasts, electronic health care, guidance and entertainment systems for cars, etc. 10% of the market is projected to be IoT apps.
MEDIUM RATE OF DATA TRANSFER:
The speed at which data is sent is less than 1 Mbps. 2G and MTC/eMTC are the connectivity methods that can be used. A POS machine, a smart home, and an M2M return link are all examples of that use. 30% of the market is expected to comprise these IoT apps. However, in the future, MTC/eMTC technology will slowly replace 2G M2M.
LOW RATE OF DATA TRANSFER:
The speed at which the data is sent is less than 100 Kbps. NB-IoT, SigFox, LoRa, and short-range radio connectivity like ZigBee are the entry technologies that can be used. They are primarily used in low-power wireless technologies, such as sensors, smart meters, tracking items, transportation, parking, and smart farming. 60% of the market is expected to comprise these IoT apps. On the other hand, there are still a lot of open positions in the related market. Because of this, NB-IoT will do well in the future.
Also read: MQTT in IoT:- Why you need it in your IoT Architecture
Ways that NB-IoT can work
1. Can be used by itself
The stand-alone mode uses a separate carrier, like the bandwidth that GSM EDGE Radio Access Network (GERAN) systems use now, instead of one or more GSM carriers. In places where cellular services aren’t available or are being turned off, this is used to make a narrow bandwidth available, like cellular GSM. Changing how one or more GSM providers work to allow NB-IoT data will make the switch to LTE for contact between many machines go smoothly.
2. The Guard Band
This mode uses resource blocks that aren’t being used in an LTE carrier’s guard band. This method is used when cellular services are available and NB-IoT is in the LTE guard band.
3. In the band
In this mode, resource blocks in a regular LTE carrier are used. This method is used when cellular services are available and NB IoT is in the LTE guard band. This way of working saves cell providers money and time because they don’t have to change hardware. Depending on what users or devices want, it also uses frequency resources for LTE or Narrowband-IoT services.
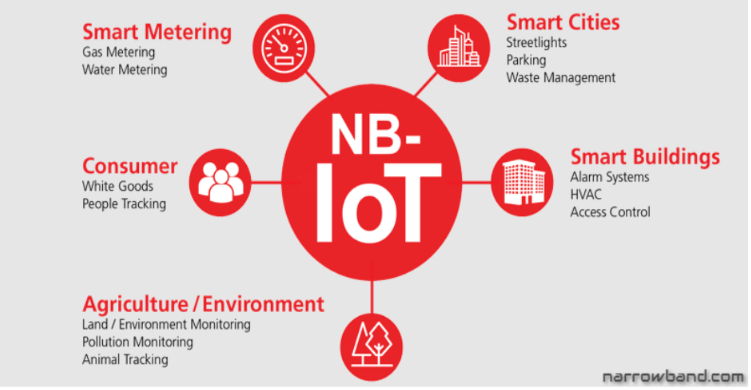
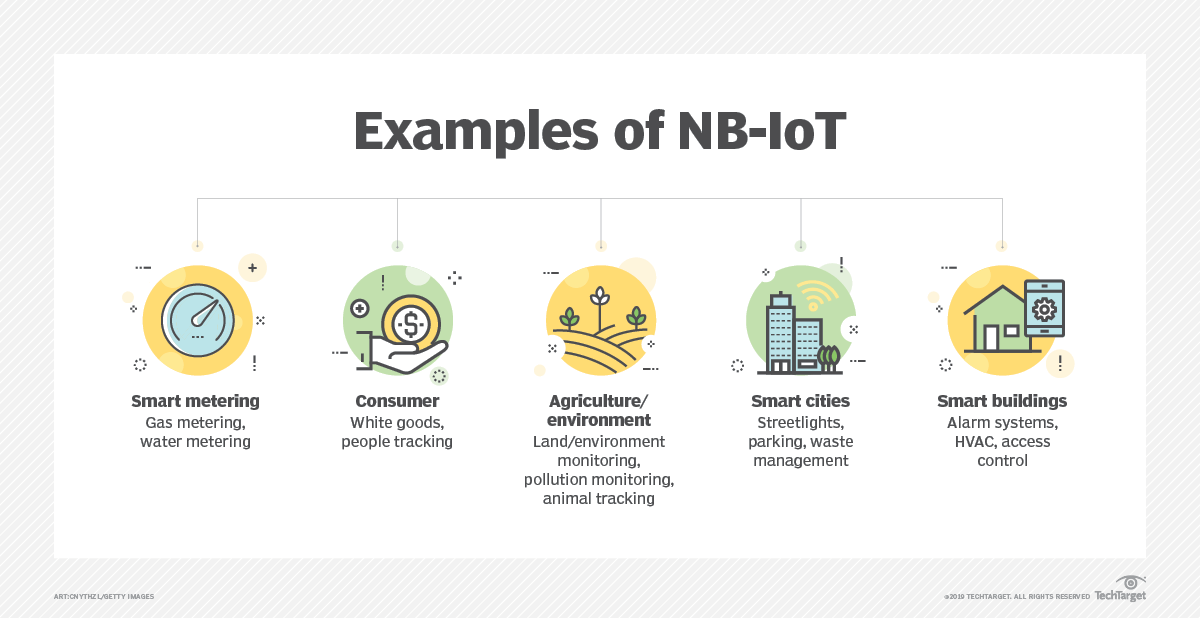
Applications and Use Cases for NB-IoT
This low-power, wide-area cellular technology can be used anywhere, from the middle of the city, where network connections are very stable, to deep underground tubes, which are much harder to get into. Many people like NB-IoT because it uses little power and doesn’t cost much, making it an easy choice for many uses.
1. With smart meters
It is possible to use advanced monitoring infrastructure with NB IoT, which lets the meter and the user talk back and forth without needing a viewer to be present. It makes it possible for owners of devices to handle and watch them from anywhere convenient for them.
2. Smart Towns
NB-IoT can be used in any way possible in intelligent towns. There are many new ways to use it, such as automatic street lighting, innovative waste management, and smart parking. Connected emergency services, weather monitoring, and traffic tracking are other uses.
3. Smart homes and business buildings
NB-IoT can connect to sensors that alert users when ideal conditions aren’t met. These sensors can be used for room temperature, smoke monitors, lighting settings, air levels in tight spaces, fire sirens, access control, and identity management.
4. Healthcare
NB-IoT technology can make connected mobile devices that measure health factors a reality in healthcare and e-health. Because older people need to have their health constantly checked, these gadgets, which mostly come in the form of trackers, are very helpful. If you want to track and examine things like Blood Pressure and Heart rate daily, NB-IoT is the most reliable and workable choice.
5. Markets for Industries
NB-IoT is a base technology used in a wide range of industrial products, from intelligent shelves in the connected retail sector to precision farming tools in the farmland sector. It makes it possible to automate industrial processes and monitor equipment in real time. This technology’s high performance can help companies and stores integrate processes and tools more effectively by letting them make decisions in real-time and work more efficiently.
6. Power and Utilities
Thanks to NB-IoT technology, it’s easy to stop people from using too much water and electricity, which cuts down on waste. This technology is beneficial when the equipment is set up in underground caves, cellars, and other dug areas. With NB IoT, it’s easy to determine what meter numbers mean, including any hidden information about waste or flow problems.
7. Agricultural Business
In the agricultural industry, it can help you make decisions based on data about your animals’ health and the growth of your goods. Smart soil sensors and analytics, which NB-IoT allows, can help handle farming tasks like watering and weeding by regularly updating the set conditions.
8. Retail Business
Thanks to NB-IoT, many parts of the retail industry have become more efficient. These include supply chain management and transportation. NB-IoT can make it easy for an organization to keep track of its assets, as long as the tracking doesn’t always happen. People think this technology works best when tracking needs to be done over a long distance and with little power.
NB-IoT has become an important technology that lets devices (standing or mobile) join wirelessly in a permitted band. As IoT devices change from static sensors to mobile sensors with delay limits, they will change the capacity of wireless networks and take advantage of the need for coverage. Strategy Analytics also thinks that by 2020, more than 3 billion linked gadgets will be in use. The option to upgrade the radio access network and set up NB-IoT services is significant for cell providers and IoT users.
Prospects for the Future
As the Next-Generation Internet of Things continues to develop, its integration with future technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Edge Computing has enormous promise for opening up new frontiers in the Internet of Things innovation. Because 5G networks will be able to enhance the capabilities of NB-IoT, the future will bring about a paradigm change toward hyper-connected ecosystems and technologically advanced automation.
Conclusion
Narrowband Internet of Things, often known as NB-IoT, is a technology that has the potential to revolutionize the Internet of Things (IoT) connection environment. Compared to typical cellular networks, it runs on a licensed spectrum, which guarantees improved coverage and a longer battery life for Internet of Things devices. It provides a multitude of advantages, including enhanced data transfer speeds, decreased power consumption, and seamless integration achieved via the use of open standards.
This technology has various applications across various industries, including smart cities, industrial automation, healthcare, and agriculture, each of which are examples. Because of its low power consumption and cost-effectiveness, it is an excellent option for smart meters, smart homes, and corporate buildings. Furthermore, by allowing real-time monitoring and data-driven decision-making, NB-IoT significantly boosts retail, utilities, and agriculture efficiency.
Narrowband-based Internet of Things (NB-IoT) is set to play a crucial part in the ongoing growth of IoT services, with forecasts showing broad use in the years to come. As a result of its cost-effectiveness and its capacity to deliver dependable connections in various situations, it is an essential enabler of the Internet of Things ecosystem at the same time. As the need for connected devices continues to rise, NB-IoT has emerged as a crucial technology driving innovation and efficiency across various distinct sectors.




