Connected devices have permeated every facet of our lives due to the proliferation of the Internet of Things (IoT), and now on to the head to revolutionize the agriculture sector. According to reports, IoT in agriculture holds a bright future, with its market set to generate $78 billion by 2023. To make the most of the IoT in agriculture, it is time to take complete leverage of it.
The Internet of Things (IoT), linked gadgets, and automation will inevitably find a home in the agricultural sector, enhancing practically every industry aspect. With self-driving cars and virtual reality becoming commonplace, how can we continue to depend on horses and plows?
Technological advancements in the previous several decades have led to a marked increase in industrialization and reliance on machinery in farming. Thanks to many smart agriculture devices, farmers now have more predictability and efficiency in their livestock and agricultural production.
This article will discuss some of the uses of the Internet of Things IoT in farming and its advantages. Put your money into smart farming or start working on an IoT solution for the agricultural sector immediately.
About Smart Agriculture Solutions
Contemporary farming can be defined in various ways. Take “AgriTech” as an example; it describes the use of technology in farming generally.
However, when people talk about “smart agriculture,” they usually mean using Internet of Things (IoT) solutions in farming. So, how exactly can the Internet of Things (IoT) make smart agriculture possible? Internet of Things (IoT) sensors may gather machine and environmental parameters, allowing farmers to enhance their operations in every area, from raising cattle to growing crops.
For example, farmers can determine the precise amount of pesticides and fertilizers to use by monitoring the status of crops with smart agricultural sensors.
Must Read: A Complete Guide To Iot Mobile App Development For Businesses
Numbers speak louder than words: Some Essential figures about IoT in agriculture-
Here, we have stats and figures about the usage of IoT in agriculture. Let’s have a look:
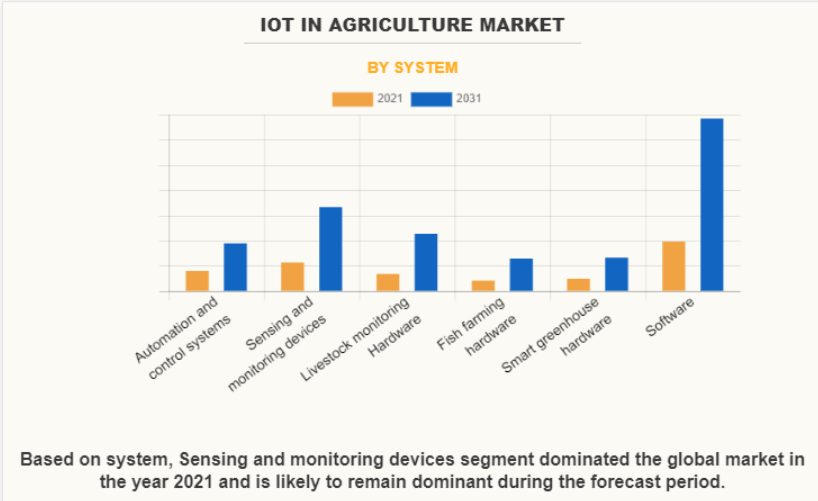
- With a population of 9.7 billion by 2050, the agriculture sector must adopt innovative technology to meet this demand.
- The global IoT in the agricultural market was valued at $27.1 billion in 2021 and is expected to reach $84.5 billion by 2031, increasing at a 12.6% CAGR between 2022 and 2031.
- The “Smart agriculture” or “smart farming” business is expected to be worth $25.4 billion by 2028, as farmers around the world strive to use RFID, GPS, drones, sensors, and other technologies to collect usable data and automate every step of the process.
Benefits of Smart Farming: How’s IoT shaping agriculture?
There are a lot of ways in which technology and the Internet of Things might revolutionize farming. The Internet of Things (IoT) can enhance farming in six specific ways:
- Smart agriculture sensors gather a mountain of data, such as the weather, soil fertility, crop development rate, and cattle vital signs. With this information, you can monitor your company’s overall health and the efficiency of your employees and machinery.
- Reduced production risks due to improved control over internal processes. Better product distribution planning is possible when production output can be predicted. You may avoid having unsold goods sit around if you know how much produce you will harvest.
- Enhanced command over manufacturing allows for better cost management and less waste. If you can monitor your crops and livestock and notice any unusual trends, you can reduce the likelihood of losing your harvest.
- Automating more corporate processes led to increased efficiency. With the help of smart devices, you may automate several activities in your production cycle, like irrigation, fertilization, and pest control. Reports predict that IoT in the agriculture market will generate a value of up to $84 billion by 2031.
- IoT technology allows you to strengthen production control, maintain high crop quality and growth capacity, and automate everything.
- Automation also benefits the environment. By providing more targeted fertilizer and insecticide applications, smart farming technologies can lessen the need for these inputs, lowering greenhouse gas emissions.
Read more: Telecom Transformation: A Deep Dive into Generative AI’s Impact
Use cases of IoT in agriculture
-
Monitoring of climate conditions
Weather stations integrate several smart agricultural sensors and are among the most widely used smart agricultural devices. Distributed around the area, they gather various environmental data and upload it to the cloud. Using the above data, one can create a climate map, select suitable crops, and implement necessary improvements to their yield (i.e., precision farming).
-
Greenhouse automation
Most farmers rely on human intervention to manage automated greenhouse conditions. However, using Internet of Things (IoT) sensors, they can receive precise, real-time data on lighting, temperature, soil condition, humidity, and other greenhouse variables.
In addition to collecting data about the surrounding environment, weather stations can automatically change their settings to fit the specified parameters. This approach is particularly used by automation systems in greenhouses.
-
Crop management
Crop management devices are another component of precision farming and an additional Internet of Things product in the agricultural sector. They should be set up in the field to gather data unique to crop farming, such as meteorological conditions, rainfall, leaf water potential, and general crop health, much like weather stations.
This way, you can monitor your crops and notice unusual growth patterns to prevent pests and illnesses that could reduce your harvest. Arable and Semios can be useful examples of practical implementations of this use case.
-
Cattle monitoring and management
Internet of Things (IoT) agriculture sensors can track the vitals and productivity of farm animals in the same way that crop monitoring tracks crop progress. Monitoring and tracking livestock allows data collection regarding the animals’ location, health, and general welfare.
For instance, farmers can use these sensors to isolate sick animals from the rest of the herd to prevent the spread of disease. Farmers can also save money on manpower by using drones to track animals in real-time. This function is analogous to Internet of Things (IoT) animal care gadgets.
-
Precision farming
Efficiency and well-informed data-driven decisions are at the heart of precision farming, also called precision agriculture. Additionally, it is among the most popular and fruitful uses of the Internet of Things (IoT) in farming.
Farmers can get a plethora of data about the field’s microclimate and ecology, including illumination, soil condition, humidity, CO2 levels, and insect infestations, using Internet of Things (IoT) devices. Thanks to this data, farmers can better predict how much water, fertilizer, and pesticide their crops will require, which in turn helps them save money while growing healthier harvests.
-
Agricultural drones
Smart farming using agricultural drones is one of the most exciting developments in agritech. Unmanned aerial vehicles, or drones, are more suited to gathering data from farms than planes or satellites. Drones can do many things that used to require humans, such as planting crops, battling diseases and pests, spraying crops, monitoring crops, and surveillance.
-
Predictive analytics for smart farming
There is a close relationship between predictive data analytics and precision farming. The Internet of Things (IoT) and smart sensor technology provide farmers with a wealth of real-time, relevant data; however, data analytics allows them to make sense of this data and make key predictions, such as when to harvest their crops, how likely they are to be infested, how much of a harvest they can expect, etc. Farming is weather-dependent by nature; data analytics techniques assist in making this process more predictable and controlled.
-
End-to-end farm management systems
“Farm productivity management systems” are a more nuanced way of looking at Internet of Things (IoT) devices in farming. Typical components include many on-site sensors and Internet of Things (IoT) devices used in agriculture, with an advanced dashboard that offers built-in accounting and reporting capabilities and strong analytical tools.
Opportunities abound in areas such as logistics, storage management, vehicle tracking (or even automation), and the Internet of Things (IoT), in addition to those already mentioned in the context of agriculture.
-
Robots and autonomous machines
Autonomous devices for farming are another area that stands to benefit from robotic advancements. Some farmers already use tractors, automated harvesters, and other self-driving machinery. These robots can accomplish difficult, repetitive, and labor-intensive tasks.
Examples of contemporary robots include autonomous tractors that may follow predetermined routes, communicate with one another through various means (such as notifications), begin operations at prearranged times, etc. Farmers may save money on labor with these driverless tractors.
In smart farming, robots also help with seed sowing, weeding, and watering. These tasks require a lot of physical effort and are quite strenuous. The gentle touch of these agricultural robots greatly lessens the toll on plants and the natural world.
-
Cost Reduction
IoT technology will enable farmers to cultivate more productive crops at a lower cost. Agriculture IoT devices may help them monitor herd health, estimate crop water requirements, and collect environmental and machine data. An IoT-based agriculture monitoring system will minimize the number of visits needed to check crop spraying, equipment performance, and arable land conditions. A smart irrigation system will assist farmers in addressing the issue of over-watered or over-dry plants. These environmental sensors will help farmers collect IoT data, improve predictive data analytics and pest management, and raise crop efficiency.
Read more: Implement Adaptive AI in Business
Things to consider before developing your smart farming solution
We can see an infinite number of use cases for IoT in agriculture. Your farm’s productivity and income can be enhanced in numerous ways with the help of smart technologies. Nevertheless, developing IoT apps for agriculture is a challenging undertaking. Before spending on smart farming, consider a few points about the challenges.
-
Technical requirement
The number one thing in making IoT app devices for agriculture is to choose what parts to include in your farm device. Choose an appropriate sampling technique based on the objective one aims to map and the general goal of the solution.
There is an immediate and direct relationship between the dependability and precision of your data acquired, depending on the quality of your sensors, which will, in turn, affect the success of your product.
-
Data Analytics
Data analytics should be the basis of every smart agriculture unit. Facts can help you appreciate reality, but if you cannot cope with this material, you will only harm yourself.
Hence, to garner information from such data, your data analysis skills must be excellent, and you must be able to deploy prediction algorithms and machine learning.
-
Maintenance team
The area where the sensors of IoT applications are located plays a major role since they are field-based; therefore, possible damage to these devices by mechanical failures will require a more sustained maintenance schedule.
To eliminate these issues, it is essential to have a maintenance team on your side to address any issues to ensure smart solutions work smoothly.
-
Feature-rich mobile support
Mobile solutions play an important role in defining the true future of smart applications in agriculture. With remote access to agriculture, farm owners and managers can easily monitor production, crop conditions, and so on. Therefore, it is essential to have feature-rich applications that support multiple devices.
Bright Future of IoT in Agriculture Industry
The Internet of Things (IoT) profoundly impacts several industries, including agriculture, which bodes well for its future. Farmers will benefit from improved decision-making, predictive analytics, and precision farming due to the increasing use of AI and ML in agricultural operations. Data collecting and monitoring will be considerably enhanced using drones and satellites.
With the Internet of Things (IoT), farmers can maximize the use of resources, lessen the impact on the climate, and adopt sustainable practices. An increasingly technologically sophisticated, resilient, and efficient future for agriculture worldwide is assured as the Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem grows, providing suitable answers to relevant problems.
Choose Parangat Technologies for top-notch IoT development in Agriculture.
IoT devices have the power to shape your farming, making it even smarter to get a glimpse of performance and farming practices. They even allow you to take safety measures well. So, get started with the best IoT development for agriculture. Parangat Technologies is your best choice, offering top-class IoT development for smart farming backed with leading features to ensure every end of farming practice is at your fingertips.
With our solutions, you will never fade off from accessing your farming from anywhere. Contact us today and choose high-end IoT development for high-quality farming.




