The digital landscape of 2024 is filled with interconnected devices that are influencing our daily lives in ways that used to exist only in science fiction. In the middle of this generation of modification lies the IoT. This guide will delve into the intricacies and wonders of IoT mobile app development, examining the current trends, challenges, and innovative solutions that characterize this year.
What is an IoT app?
IoT apps often include features like data visualization, allowing users to interpret information from sensors in a user-friendly format. They may also support customization and automation, letting users set rules for device behavior.
Security is a key consideration, with encryption and authentication measures implemented to protect the data transmitted between devices and the app. Overall, Generative AI Software Development Company contributes to the seamless integration of smart devices into everyday life, enhancing efficiency, convenience, and connectivity.
Overlook at the IoT App Market
In 2024, the IoT App Market will be a dynamic environment filled with innovation, competition, and growing adoption rates. The intertwining of the digital world with our physical surroundings presents a complex landscape of trends and insights. Let’s delve into it briefly:
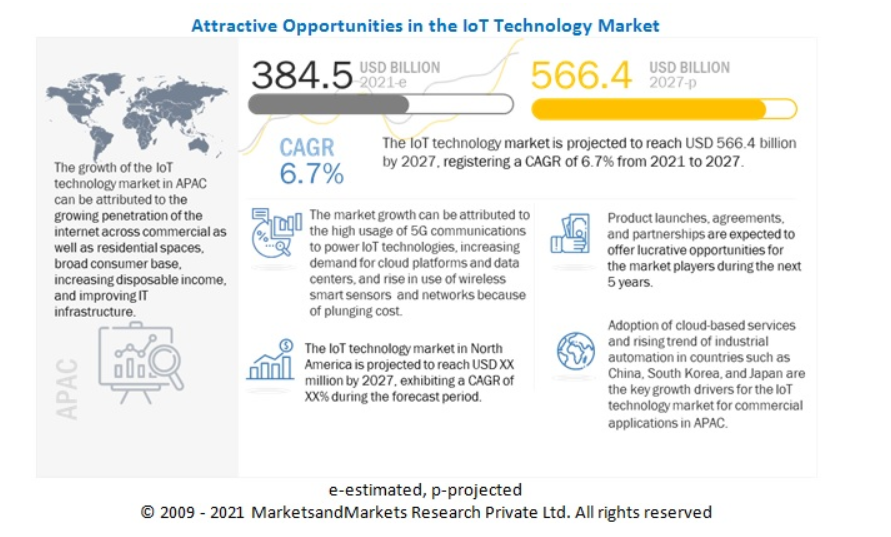
Dominant segments
The industrial IoT (IIoT) sector is earning traction, especially in areas like agriculture and healthcare, promising improved functioning efficiency amid the preponderance of smart homes.
Regional focus
While North America and Europe continue to lead the market, the Asia-Pacific region, containing China and India, is swiftly catching up with noteworthy improvement.
Key player
Established tech giants such as Google, Amazon, and Microsoft hold sway, yet startups are introducing novel solutions tailored to specific niches within the IoT domain.
Investment trends
The venture capital budget for IoT startups is at its peak, and a surge in unions and investments contemplates a growing market landscape.
Consumer trends and expectations
Users are seeking user-friendly interfaces, robust security measures, and seamless integrations in IoT applications, leading to increased adoption rates when these demands are met.
Challenges and prospects
The IoT app market is confronted with challenges related to data privacy and device compatibility. Generative AI Development initiates standardization and advanced security solutions pointing towards a promising sector outlook.
Key Components in IoT App Development
Crafting an IoT application is not a simple task. It necessitates the careful coordination of numerous components, with each one carrying significant importance in guaranteeing the smooth operation of the IoT application. Let’s explore in more depth these essential components:
Hardware
In IoT app development, hardware components refer to the physical devices that make up the IoT ecosystem. Key components include:
-
Sensors and Actuators
These devices capture real-world data (sensors) or perform physical actions (actuators). Motors, motion detectors, and temperature sensors are several examples.
-
Microcontrollers/Microprocessors
These are the brains of IoT devices, responsible for processing data and controlling device functions. Common examples include Arduino boards, Raspberry Pi, or specialized microcontrollers.
-
Communication Modules
Devices need a means to transmit data to and receive commands from the IoT app. Communication modules such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, or cellular modules facilitate this connectivity.
-
Power Supplies
Depending on the application, devices may use batteries, power over Ethernet (PoE), or other power sources. Power efficiency is critical for IoT devices with limited energy resources.
-
Embedded Systems
These are specialized computing systems integrated into devices. They include both hardware and software components, enabling specific functionalities.
-
Gateways
In larger IoT deployments, gateways act as intermediaries between devices and the central server or cloud. They aggregate data from multiple devices and facilitate communication.
Connectivity
Connectivity in IoT app development involves the technologies and protocols that enable communication between IoT devices and the application. Key components include:
-
Wireless Protocols
IoT devices often communicate wirelessly. Common protocols include Wi-Fi for high-speed data transfer, Bluetooth for short-range communication, Zigbee and Z-Wave for low-power, low-data-rate applications, and cellular networks for wide-area coverage.
-
MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport)
A lightweight and efficient messaging protocol intended for low-bandwidth, high-latency, or unstable networks. MQTT is widely utilized in IoT because of its publish-subscribe mechanism.
-
HTTP/HTTPS
Devices can communicate with the IoT app using standard web protocols. This is common for cloud-based IoT solutions where devices send HTTP requests to APIs for data exchange.
-
CoAP (Constrained Application Protocol)
Designed for resource-constrained devices, CoAP is a lightweight protocol suitable for IoT applications, especially in scenarios where low power consumption is crucial.
-
LoRa (Long Range)
A low-power, wide-area network (LPWAN) technology suitable for long-range communication with low data rates. It is often used in applications like smart agriculture and industrial IoT.
-
5G
The fifth generation of mobile networks, 5G, provides high-speed, low-latency communication, making it suitable for IoT applications requiring real-time data processing and high bandwidth.
IoT platforms
Cloud solutions aiding IoT functionalities include a variety of services like device management, data ingestion, processing, and analysis.
-
Amazon’s AWS IoT
It delivers a comprehensive suite of features, spanning from the edge to the cloud, guaranteeing smooth device connectivity and security.
-
Microsoft’s Azure IoT platform
It is recognized for its scalability, providing a diverse array of services that address various IoT requirements, from simple setups to intricate environments.
-
Google Cloud IoT
It presents a sturdy platform offering holistic solutions embedded with advanced AI and machine learning capabilities, enabling the extraction of valuable insights from data.
Data management
The influx of data from various devices necessitates the importance of storage and analysis.
-
Cloud storage
Scalable and secure solutions for storing vast volumes of IoT data are provided by cloud storage platforms such as AWS S3, Google Cloud Storage, and Azure Blob Storage.
-
Analytics tools
After storing data, extracting insights becomes crucial. Tools like Google’s BigQuery, AWS’s Redshift, and Azure’s Stream Analytics aid in analyzing data to enhance IoT functionalities and user experience.
Also read: Explore The Potential Of AI And IoT Technologies In The Business Sectors
Cost of IoT Mobile App Development
Businesses considering IoT mobile app development must prioritize understanding the costs involved. Various elements contribute to the final price tag, making it essential to grasp them. The multifaceted nature of generative AI development services projects requires a comprehensive understanding of associated costs. Optimizing costs involves analyzing and managing the components contributing to the overall price. Determining factors include:
Complexity:
Integrating more features and functionalities in an IoT app increases development costs. Factors like the number of supported devices, data processing needs, and user interface intricacies influence the complexity.
Hardware:
IoT involves interconnected devices with sensors, actuators, and boards. The type and number of these components influence the cost. Custom-designed hardware components can increase expenses.
Software:
The app is a software component. Additional costs may arise from licensing third-party platforms or services, using premium cloud storage solutions, and opting for specialized analytics tools.
Services:
Costs for IoT applications go beyond development and can include maintenance, updates, support, and training. Ongoing services can comprise a significant portion of the budget, depending on the nature of the IoT application.
Estimation: basic vs. advanced IoT apps
In the realm of IoT applications, there are two main classifications based on their complexity and functionalities.
Basic IoT applications
These applications tend to have limited features and support only a small range of device types. They often utilize readily available hardware components and are designed for simple tasks like data logging or basic device management. The development cost for these apps is typically lower, usually within the range of $15,000 to $50,000.
Advanced IoT applications
On the other end of the spectrum, advanced IoT apps are all-encompassing solutions that cater to diverse device types and involve intricate data processing. They boast advanced user interface and user experience designs and may even incorporate custom hardware components. These applications are commonly tailored for industrial IoT requirements, smart city initiatives, or groundbreaking innovations in the healthcare sector. The development costs for advanced IoT apps can vary significantly, with high-end solutions often surpassing the $200,000 mark.
Tips for budgeting and reducing costs
Tips for budgeting and reducing the cost of building an IoT app are mentioned below:
1. Prioritize features
By starting with a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) strategy, prioritize the essential functions of your IoT app. Gather user feedback after launch and incrementally introduce new features. This approach not only minimizes initial expenses but also ensures that the added features align with user preferences.
2. Capitalize on open-source resources
Take advantage of the vast array of open-source platforms and tools within the tech community to reduce licensing expenses significantly.
3. Streamline cloud costs
Cloud services typically operate on a pay-as-you-go basis. Consistently reassessing and optimizing your usage can lead to considerable cost reductions.
4. Ensure regular upkeep
While investing in routine maintenance may appear as an additional expense, it can ultimately save money by averting costly downtime or security breaches in the future.
Challenges & Solutions in IoT App Development
IoT application development comes with challenges due to the expanding IoT landscape. Developers and businesses face obstacles that need to be understood and appropriately addressed for the success and security of Generative AI development services initiatives.
Security concerns
Challenge:
As the number of interconnected devices continues to rise, the threat of security breaches also escalates. The IoT ecosystem faces significant risks, such as unauthorized entry, data infringement, and manipulation of devices.
Solution:
To address these challenges effectively, it is crucial to establish strong security protocols across all levels. This involves adopting end-to-end encryption, regularly updating firmware, and employing secure communication standards. Additionally, enhancing security can be achieved by incorporating advanced authentication techniques such as biometric or multi-factor authentication.
Device interoperability and scalability
Challenge:
In a landscape filled with a diverse range of IoT devices boasting unique specifications, communication protocols, and standards, navigating significant compatibility obstacles is inevitable. This hurdle becomes particularly apparent when expanding operations or harmonizing various devices in an interconnected system.
Solution:
To overcome this challenge, embracing universal standards and communication protocols emerges as a viable solution. For instance, entities such as the Open Connectivity Foundation (OCF) dedicate efforts to formulating these universal specifications. Additionally, implementing middleware solutions, functioning as intermediaries that decode and transmit data across devices, stands out as an effective approach to easing interoperability concerns.
Real-time data latency
Challenge:
For various IoT applications, especially those related to health or safety, instant data transmission plays a vital role. The repercussions of even the slightest delay or latency can be significant.
Solution:
The answer lies in the rise of edge computing within this field. By handling data near its origin, which is usually the device, the latency is minimized. Enhancing the network infrastructure, choosing effective communication protocols, and guaranteeing efficient data pathways are key factors in attaining instantaneous data processing and transmission.
IoT App Development Trends
Understanding the trends in Generative AI development solutions is essential for businesses to remain relevant. The most prominent trends in IoT app development this year should be explored.
1. Edge computing
Trends:
IoT devices typically transmit data to centralized cloud servers for analysis. Nevertheless, the growth in device numbers and the massive amount of data produced have indicated drawbacks to this approach. This is where edge computing comes into play. It handles data in proximity to where it originates, either on the device directly or on nearby servers.
Implications:
This change notably decreases delays, guarantees quicker reaction periods, and eases the burden on primary servers. Particularly for scenarios that demand immediate data analysis, like self-driving vehicles or health monitoring systems, edge computing is demonstrating its revolutionary capabilities.
2. AI and AR/VR integration
Trends:
The emergence of Artificial Intelligence (AI) has been causing a stir in various sectors, and its fusion with IoT stands out. There is a growing trend of intertwining Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) with IoT applications.
Implications:
AI boosts the functionalities of IoT gadgets, empowering them to independently make decisions based on data trends. Take, for instance, the ability of smart thermostats to analyze user behaviors and adjust accordingly. On the other hand, AR and VR are enhancing user engagement. Picture an AR application assisting a user in configuring an IoT device or a VR platform that enables users to interact with their smart home configurations.
3. Blockchain for security
Trends:
Blockchain technology is seen as a potential remedy for the security challenges arising from the decentralized structure of IoT networks. Its appealing qualities of transparency and security render it a favorable choice for addressing these concerns.
Implications:
The integration of blockchain ledger development in IoT networks enables the secure documentation of transactions and data exchanges, guaranteeing the immutability of records. This heightened level of data integrity and security is a significant benefit. The use of smart contracts can automate interactions among devices, ensuring adherence to predefined conditions before the execution of actions.
Conclusion
Companies must keep pace with the changing trends to remain relevant in the fast-moving industry. Utilizing the full potential of IoT is not only a strategic move but a necessity in today’s dynamic environment. Keep in mind that your business’s transition to digitalization is just one consultation away. Collaborate with Parangat to transform your IoT app concepts into innovative solutions.




